Context
Context
 Science
Science
 Noteworthy
Noteworthy
- Clinical Need
- Current Solutions
- Safety Issues
- Regulatory Response
- Patients and Physicians
- Environmental Impact
- Motivation
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- MRI Contrast Agents
- Gadolinium vs Manganese
- Reveal: The Gadolinium-Free Contrast Agent
- Clinical Need
- Over 30 million contrast-enhanced (CE) MRI scans are performed worldwide each year; a total of 450 million CE-MRI scans to date. CE-MRI scans provide information that is not available with any other methodology, granting vital medical insight that informs diagnosis and management of cancer, cardiovascular disease, Crohn's disease, multiple sclerosis, myeloma, stroke, various genetic disorders, and many other conditions.
- Current Solutions
- All current MRI contrast agents are based on gadolinium, a rare earth element which is alien to biology. Gadolinium is a potent calcium antagonist and is highly toxic in its ionic form. Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) utilize chelating ligands to bind the metal and render it less toxic for intravenous administration. Despite this even the most stable GBCAs release some gadolinium.
- Safety Issues
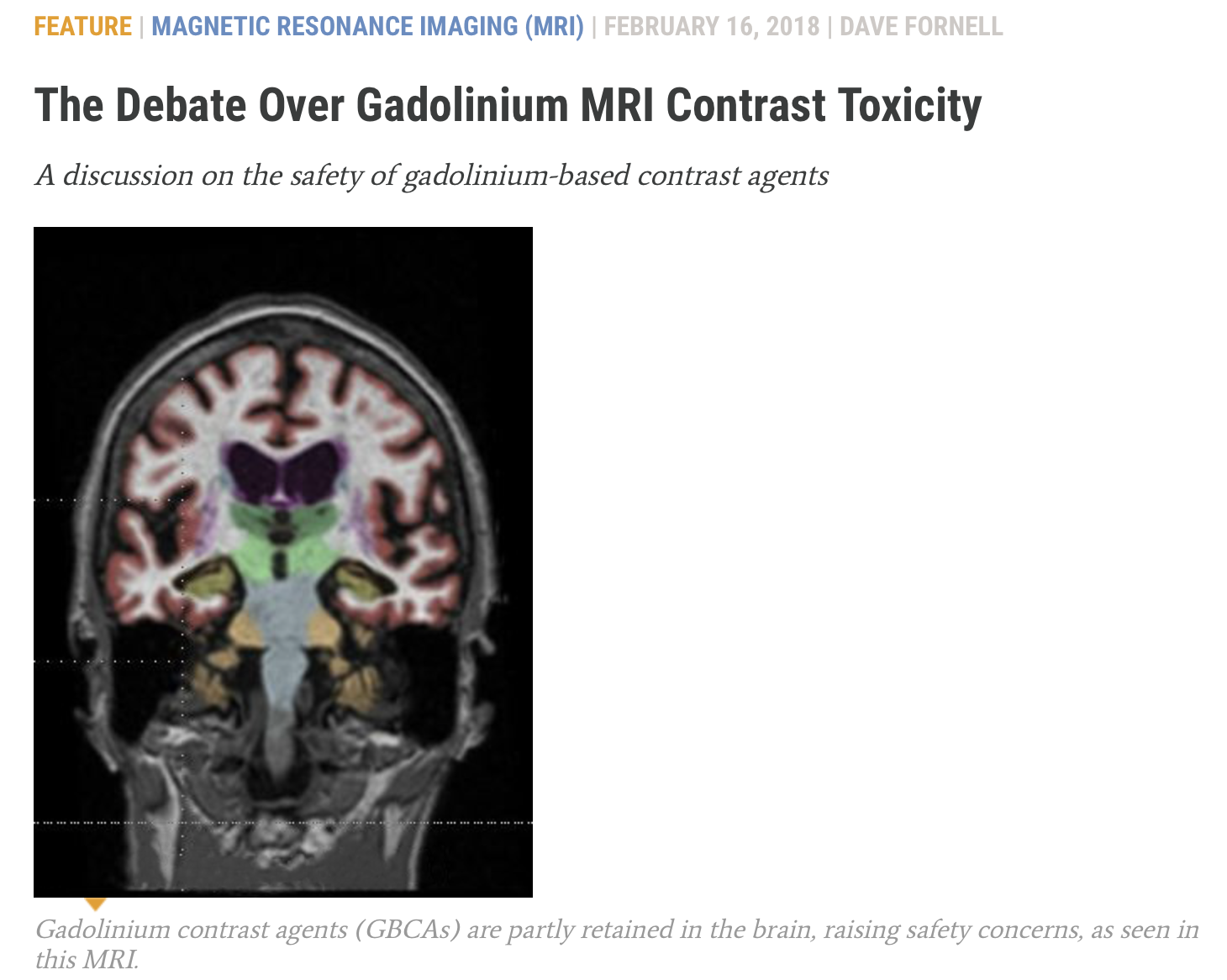
- In 2006 it was found that GBCAs trigger devastating nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in renally impaired patients. Subsequently, deposition of gadolinium in bone, skin, and other organs was documented. In 2013 it was discovered that GBCAs cause cumulative gadolinium deposition in the brains of all patients regardless of renal function. Studies have shown that all GBCAs cause deposition of gadolinium in the brain, bone, and other organs of all patients. Studies are ongoing and concern is rising about the biological activity, toxicity, and potential late effects of gadolinium.
- Regulatory Response
- The FDA instituted a boxed warning on all GBCAs in 2007, cautioning that they should not be used in renally impaired patients due to the risk of NSF. After the discovery of brain deposition of gadolinium, worldwide regulators responded with suspensions, restrictions, label changes, and safety warnings. There is continuing unease and uncertainty about GBCAs. Even the most stable GBCAs release gadolinium which is deposited in the brain, bone, and other organs, and remains in the body indefinitely. The long term biological activity of gadolinium – and consequent implications for patients – are not well understood.
- Patients and Physicians
- People with significant health conditions frequently require contrast enhanced imaging to guide diagnosis and clinical management. Accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment may dramatically improve each patient’s prognosis and quality of life.
However, many people who are gravely ill also have kidney dysfunction and are contraindicated for all current MRI and CT contrast agents. As a result these patients are either inadequately assessed or are put at risk from contrast agents.
Gadolinium deposition in the brain, bone, and other organs affects all patients. People at highest potential risk from GBCAs include children, those with renal impairment, and people who require repeated CE-MRI scans for surveillance, ongoing disease management, or clinical trials. e.g. brain cancer survivors, women at high risk of breast cancer, many cancer patients, people with cardiorenal syndrome, chronic kidney disease, Crohn's disease, multiple sclerosis, myeloma, and certain genetic disorders.
CE-MRI provides critical medical information which often cannot be obtained using other methods. Patients and physicians face a dilemma: balancing the risks posed by GBCAs with the need for important medical imaging. Individual decisions on whether or when to use GBCA-enhanced MRIs should be based on thoughtful consultation between patients and their physicians. - Environmental Impact
- Increasing use of CE-MRI has resulted in rapidly rising levels of gadolinium in water around major metropolitan areas. GBCAs enter the sewage system when they are excreted after CE-MRIs. GBCAs are not removed by standard waste water treatment methods: consequently the GBCAs remain in the clear water discharge from sewage treatment plants and are transferred to surface water, where they reenter the agricultural and urban drinking water supply, and ultimately find their way to the ocean. Unlike biocompatible elements, gadolinium has no established ecological cycle. The biological activity of the rising amount of gadolinium in the aquatic ecosystem is just beginning to be explored, and has unknown consequences for downstream human health.
- Motivation
- The impact of contrast enhanced (CE) MRI is enormous, with more than 30 million CE-MRI scans worldwide each year, and over 450 million CE-MRI scans performed to date. Like so many others, Reveal’s team has been personally impacted by the benefits of – and concerns surrounding – contrast-enhanced MRI.
Peter Caravan and Eric Gale set out to invent a contrast agent that would be safe for people with renal impairment, who are often contraindicated for current CT and MRI contrast agents. As more concerns around gadolinium retention were discovered it became clear that all patients need a safer contrast agent that does not deposit gadolinium in their brains, bones, and other organs.
Our goal is a safer MRI contrast agent for all patients. - Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a sophisticated non-invasive imaging technology which produces detailed three-dimensional images of internal anatomy. MRI contrast agents typically increase MRI signal and create greater contrast between different tissue types or between normal and diseased tissue. Contrast-enhanced MRI often provides information that cannot be obtained without contrast agents. CE-MRI is used to detect disease, provide prognosis, guide treatment planning, and to monitor therapeutic interventions.
- MRI Contrast Agents
- MRI contrast agents alter the signal in tissue via their influence on the local magnetic environment. The best MRI contrast agents are strongly paramagnetic (i.e. they become temporarily magnetized when placed in a magnetic field) and are able to influence the orientation of water nuclei in tissue, amplifying the MRI signal. Gadolinium and manganese are uniquely suited for MRI because they are paramagnetic and each have a half-shell of unpaired electrons, producing a strong magnetic moment.
Free metal ions are reactive and may have toxic effects. To improve safety, organic molecules (ligands) are used to bind (chelate) the metal ion. To enable a strong MRI signal, these chelating agents leave an open location for a water molecule to temporarily bind. Rapid exchange of this bound water with water molecules in the surrounding tissue amplifies the MRI signal, increasing contrast. - Gadolinium vs Manganese
- Gadolinium (Gd3+) is a large, strongly charged ion which is very similar in size to calcium (Ca2+). Gadolinium readily forms relatively stable chelates allowing sufficient space for water exchange. For this reason gadolinium was historically chosen as the paramagnetic ion for most MRI contrast agents. However, gadolinium is alien to biology and there are no natural mechanisms to control and manage Gd3+ should it be released from its ligand. Free gadolinium is toxic: it is a potent calcium antagonist, irreversibly outcompeting calcium in biological processes.
Manganese (Mn2+) is an essential element which is vital for life. It is regulated by natural mechanisms and is readily processed, transported, and excreted by the body. Mn2+ is smaller and more weakly charged than Gd3+. Consequently it is challenging to create stable Mn2+ complexes that allow space for water exchange.
The MRI contrast agent Teslascan was based on manganese. Teslascan dissociated after administration and the resulting free Mn2+ ion was rapidly excreted via the liver. Teslascan was approved as a liver-specific MRI contrast agent by the FDA and the European Medicines Agency in 1997, but its rapid dissociation made it unsuitable for use as a general purpose contrast agent. - Reveal: The Gadolinium-Free MRI Contrast Agent
- Given the safety issues of gadolinium-triggered nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and deposition of gadolinium in the brain, bone, and other organs, it is clear that a safer MRI contrast agent should be gadolinium-free. The essential element manganese is the obvious biocompatible alternative to gadolinium, but is accompanied by the technical difficulty of achieving both stability and a strong MRI signal.
Peter Caravan and Eric Gale set out to solve this challenge by designing a unique chelating ligand with a cage structure to capture and securely hold the manganese ion while maintaining an open location for water exchange. To further enhance safety for people with renal impairment, they designed the new contrast agent to have a dual excretion path via both the liver and kidneys. Working at the Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging and the Institute for Innovation in Imaging at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, they invented a new class of contrast agents, with the archetype MnPyC3A.
Reveal’s contrast agent, RVP-001, draws on this work. We are advancing RVP-001 toward clinical use, where it has the potential to benefit millions of patients worldwide.
- Reveal enters Phase 1a clinical study:
First gadolinium-free general purpose MRI contrast agent to enter clinical trials
- Reveal selected as a 2022 winner of MassVentures' START Stage 2
- Reliance on China for contrast agent supply chain disrupts patient scans Patients Face Long Delays for Imaging of Cancers and Other Diseases
- Magnevist is withdrawn from the US market: The applicants notified the Agency in writing that the drug products were no longer marketed and requested that the approval of the applications be withdrawn
- The Wall Street Journal: A question for anyone getting an MRI
- FDA Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee: Potential risk of gadolinium retention: September 2017 meeting materials
- European Medicines Agency: July 2017 ruling restricts and suspends gadolinium-based contrast agents
- National Organization for Rare Diseases: Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis
 Reveal Results
Reveal Results
Mn-PyC3A has different pharmacokinetics and is more efficiently eliminated than Mn-DPDP in normal rats.
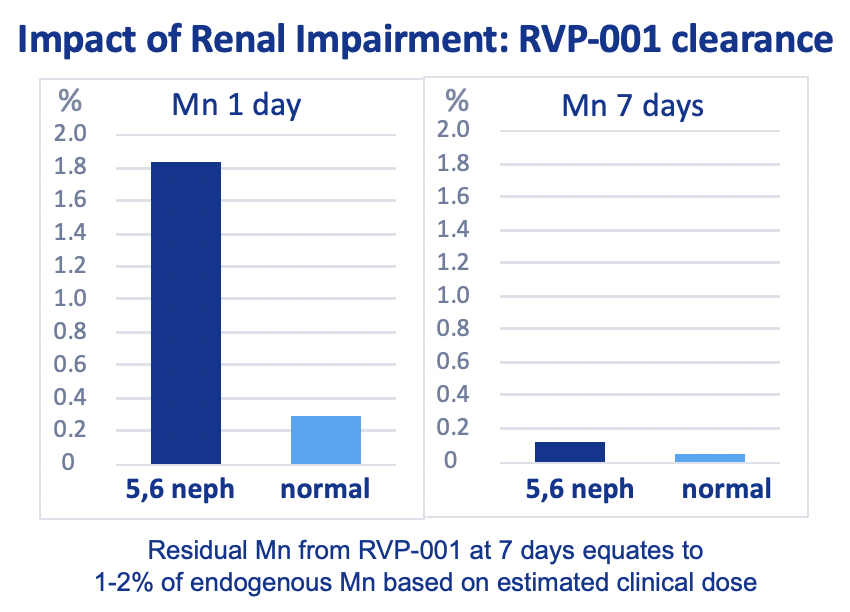
Mn-PyC3A is efficiently eliminated from both normal and 5/6 nephrectomy rats, with increased fractional hepatobiliary excretion from 5/6 nephrectomy rats.
Mn-PyC3A is more completely eliminated than Gd-DOTA from 5/6 nephrectomy rats after 7 days.
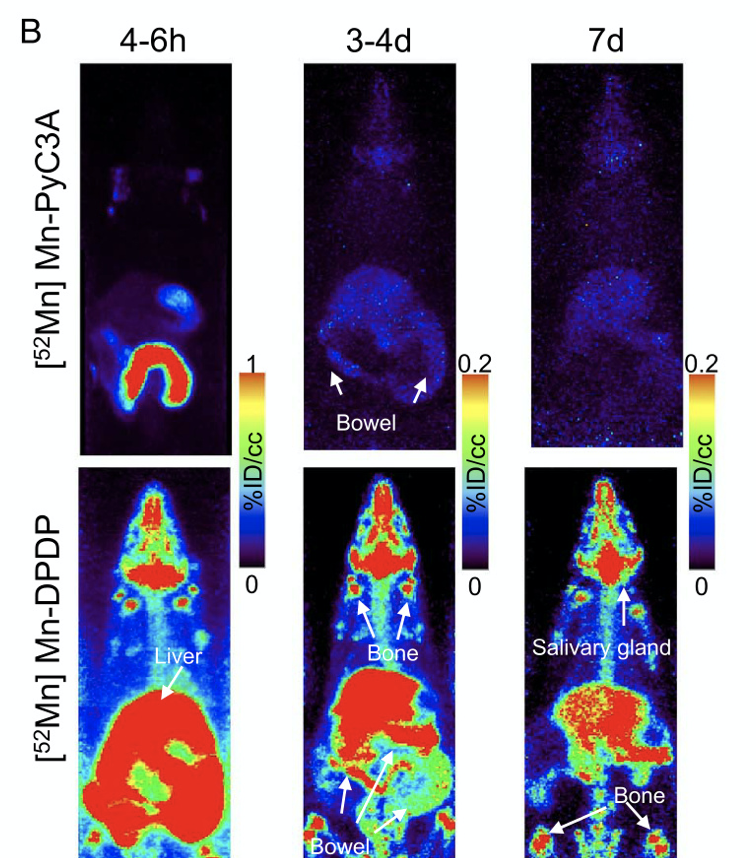
Dynamic and delayed phase PET/MR results confirm rapid renal and hepatobiliary clearance of Mn-PyC3A in both normal and 5/6 nephrectomized rats with nearly complete elimination within 24 h.
Mn-PyC3A provides comparable tumor contrast enhancement to Gd-DOTA in a mouse breast cancer model and is more completely eliminated than Gd-DOTA; partial hepatobiliary elimination of Mn-PyC3A enables conspicuous delayed phase visualization of liver metastases.
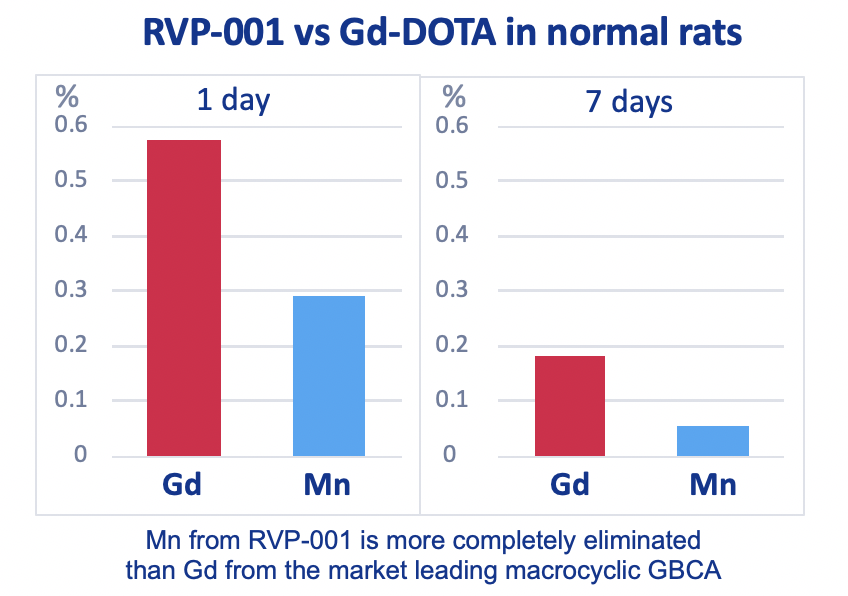
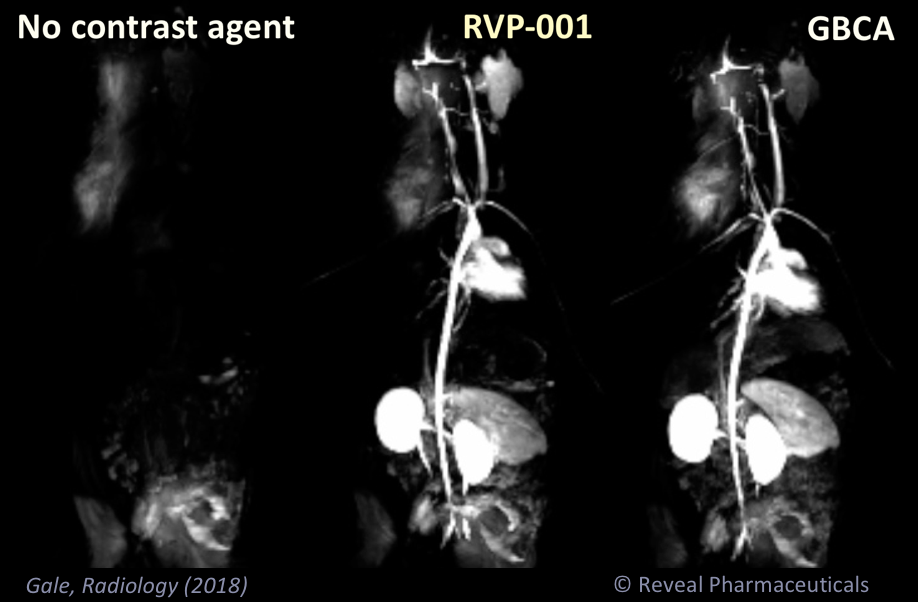
Mn-PyC3A enables contrast-enhanced MR angiography with comparable contrast enhancement to gadolinium-based agents and may overcome concerns regarding gadolinium-associated toxicity and retention.
A Manganese Alternative to Gadolinium for MRI Contrast
We present the new manganese(II) complex Mn-PyC3A as a Gd alternative.
+ Mn-PyC3A is among the most stable Mn(II) complexes at pH 7.4.
+ Relaxivity of Mn-PyC3A in blood plasma is comparable to commercial Gd contrast agents.
+ Mn-PyC3A clears via a mixed renal/hepatobiliary pathway with >99% elimination by 24 h.
+ Mn metabolite analysis reveals no evidence of dechelation and the probe was >99% eliminated after 24 h.
+ (Targeted derivative) Mn-FBP provided equivalent thrombus enhancement to the Gd analogue, EP-2104R.
 Research
Research
"Whichever contrast agent was used, some gadolinium was detectable in every organ."
"Interestingly, some low levels of gadolinium were found in the skin and [brain] of control animals, indicating probable environmental contamination."
Read Dr. Clément's editorial on gadolinium retention and how much we actually know. https://t.co/oTd9FEghhH @HegpClementO @HopitalPompidou @parcc_inserm https://t.co/8hpNfuoOD3
— Radiology (@radiology_rsna) September 28, 2021
"Gd may represent an environmental threat and a risk to human health, demonstrating the need for further research on Gd toxicity towards aquatic wildlife and the necessity for new water remediation strategies"
This study revealed significantly lower intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) for all GBCAs compared with the control group (P < 0.0001). Given the highly significant findings of the current [rodent] study, more research in this field is required.
It might be wise to shift the main focus of research into gadolinium deposition from the brain to the skin and its innervation, particularly in light of the growing evidence from the latest animal studies #Radiology #Imaging https://t.co/BsIpX6s1ob
— ISR Radiology (@ISR_Radiology) August 31, 2020
Brain MRIs make up the bulk of the gadolinium footprint in medical imaging. Comparing regional practices in France between public and private hospitals for each organ specialty. In @JNeuroradiology here: https://t.co/a810jXJQWr #MRI #Brain #Gadolinium pic.twitter.com/JLUBcjzmnX
— Elsevier Radiology (@ELS_Radiology) August 11, 2020
Gadolinium occurs in nature along with 16 other elements known collectively as rare earth metals: these rare earth metals are difficult to separate ... The presence of these elements may pose a risk for patients.
Presence of other rare earth metals in gadolinium-based contrast agents #talanta #analyticalchemistry https://t.co/bY8aOrq2dZ pic.twitter.com/LqeynM8n9V
— Elsevier Chemistry (@ELSchemistry) July 14, 2020
The increasing use of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) for magnetic resonance imaging is leading to widespread contamination of freshwater and drinking water systems. Contrary to previous assumptions that GBCAs are stable throughout the water cycle, they can degrade. Degradation products in drinking water supplies can increase the risk of adverse health effects.
Gadolinium in drinking water. Researchers from the @Hofmann_Lab suggest how to prevent this contamination. https://t.co/lqsqM3UwdF pic.twitter.com/Q1WhpE4xqt
— Hofmann_Lab (@Hofmann_Lab) June 30, 2020
The use of gadolinium base contrast agents in patients with severe chronic kidney disease or hemodialysis continues to be a subject of debate. You may be interested in this editorial that we just published giving the nephrology perspective on this https://t.co/ubjVfNA1HX
— Michael Rudnick (@MichaelRudnick7) June 25, 2020
Patients with Crohn’s disease (CD) undergo multiple gadolinium-based contrast agent injections across their lifespan ... Crohn's Disease patients are prone to gadolinium accumulation in the brain.
Patients showed significantly decreased resting-state functional connectivity (p < 0.05, FWE corrected) of several regions of the right frontoparietal (FPR) and the dorsal attention (DAN) resting- state networks.
Within-network brain connectivity in Crohn's disease patients with gadolinium deposition in the cerebellum. https://t.co/xcz5P1MIpD
— MRI Biomarkers for CKD (@renalMRI) April 5, 2020
Despite their ubiquity, gadolinium-based contrast agents are not without risks.
— JACR (@JACRJournal) April 15, 2020
Learn about the latest one that has joined the ranks. #JACR ➡️https://t.co/4E32QmUxsm⬅️ pic.twitter.com/pogTT3WsUw
Mariane Le Fur @MGHMartinos @i3MGH on how to noninvasively measure the whole body distribution of #gadolinium #mri contrast agents. Just in time for #RSNA2019 @MGHImaging #MGHRSNA https://t.co/fZZX48dy0a
— Peter Caravan (@PeterCaravan) December 2, 2019
"Repeated gadopentetate dimeglumine exposure is associated with gadolinium retention in specific regions, subregions, and layers of cerebral cortex that are critical for higher cognition, affect, and behavior regulation, sensorimotor coordination, and executive function."
Gadolinium was long thought to bypass the blood-brain barrier before settling in certain brain regions, but these findings suggest contrast may traffic alternate routes, potentially via the brain’s neurons and glial cells @RadiologyACR #gadolinium #GBCA https://t.co/irudSsEcoa
— Health Imaging (@HealthImaging) November 26, 2019
RADIOLOGY Commentary: Dr. Kanal explains new research findings on gadolinium brain deposition. https://t.co/gGvzB1PYqV #MRI #radiology @radiology_rsna pic.twitter.com/oh5B7fAaJr
— David Bluemke (@RadiologyEditor) November 26, 2019
Our preprint @biorxivpreprint with @ruppweb describing dehydration of afamin and how it binds the MRI contrast agent gadolinium is now published @ActaCrystD congrats to @PaulineJYX and @jvonvelsen ! Data collection @ID30_MASSIF1 @esrfsynchrotron @embl 👉 https://t.co/lAtjq6GVGi pic.twitter.com/okxnmujb66
— Matthew Bowler #FBPE (@moncourvoisier) November 27, 2019
"we appear to be headed into an exciting period of technology evolution in the field of MRI contrast agents."
RADIOLOGY Commentary: Dr. Michael Tweedle: Will the next generation of MRI agents include gadolinium? https://t.co/KSkpErCV3x #MRI #radiology @radiology_rsna pic.twitter.com/PY2mjAqfEY
— David Bluemke (@RadiologyEditor) November 1, 2019
"Gadopiclenol at 0.05 mmol/kg yielded comparable change in contrast-to-noise ratio and morphologic characterization of brain tumors compared with gadobenate, gadoterate, or gadobutrol at 0.1 mmol/kg."
How does the contrast-to-dose relationship of gadopiclenol, a high relaxivity macrocyclic GBCA, compare to gadoterate, gadobenate, and gadobutrol? Robert et al report their findings in a rat brain tumor model. https://t.co/TMyAUYa1HI #NeuroRad pic.twitter.com/KCnDQ7e4Wi
— Radiology (@radiology_rsna) October 30, 2019
5/ Key notes on new GBCA (gadopiclenol)
— Reveal Pharma (@revealpharma) November 7, 2019
Higher relaxivity than old GBCAs
Cerebellar Gd deposition similar to gadobutrol (not noted as the lowest)
Different structure & pharmacokinetics to other GBCAs
Peak enhancement 2-3x slower than other GBCAs
Tbd how it acts in human tumors
"A significant T1 SI increase reflecting gadolinium retention in the brain was detected for children with at least three gadoterate meglumine administrations"
3/ Concerning news about Dotarem [& Clariscan], often perceived as a ’safer’ GBCA@jmri_ismrm https://t.co/tQWarH4jH2 pic.twitter.com/wunz2vogyG
— Reveal Pharma (@revealpharma) November 7, 2019
FDA approves the ANDA for GE's "Clariscan", a generic version of gadoterate meglumine, i.e. Guerbet's Dotarem.
FDA clears Clariscan macrocyclic gadolinium-based contrast agent for #MRI scans from @GEHealthcare. #radiology https://t.co/3jbuRtjMnf
— AuntMinnie.com (@AuntMinnie) November 4, 2019
"Mn-PyC3A provides comparable tumor contrast enhancement to Gd-DOTA in a mouse breast cancer model and is more completely eliminated than Gd-DOTA; partial hepatobiliary elimination of Mn-PyC3A enables conspicuous delayed phase visualization of liver metastases."
Current Issue: Tumor Contrast Enhancement and Whole-Body Elimination of the Manganese-Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Mn-PyC3A https://t.co/Xbaomdv1MN
— InvRadiologyOnline (@InvRadiologyOnl) October 24, 2019
"The scientific debate about this finding is kept alive by the fact that SI differences do not unequivocally represent the amount of gadolinium retained.
... every effort should be made to protect patients from any side effect related to retention or exposure to GBCAs, and concern for public safety is paramount, particularly in children and patients who need several follow-up exams."
This position paper from the European #Gadolinium Retention Evaluation Consortium (GREC) Task Force position statement provides useful thoughts for analysis of this worrying situation, and the basis for future studies.#EurRadiol
— ESR Scientific Publications (@ESR_SciPub) October 17, 2019
Click here to read more: https://t.co/mvsZVYIK8u pic.twitter.com/DYOZhCp8EB
FDA research - "This study identified higher rates of gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) exposure during the first few weeks of pregnancy, suggesting inadvertent exposure to GBCAs might occur before pregnancy is recognized."
Some #pregnant women may be inadvertently exposed to gadolinium-based contrast agents early in their pregnancies, according to a new study published in @radiology_rsna: https://t.co/SGhCgbA3Fz #MRI #RadSafety pic.twitter.com/GAcURE5WwG
— RSNA (@RSNA) August 20, 2019
"GAP is likely on a spectrum of fibrotic skin conditions associated with gadolinium exposure, similar to NSF."
Gadolinium‐associated plaques (GAP) is a newly described condition associated with prior gadolinium‐based contrast exposure. There is an absence of other clinical features seen in nephrogenic #systemic #fibrosis. Free access: https://t.co/wWHjpMOTOE pic.twitter.com/1LEKVdFO91
— BJD (@BrJDermatol) August 3, 2019
"These results demonstrate a toxic effect of gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents on mitochondrial respiratory function and cell viability."
Current Issue: Gadolinium-Based MRI Contrast Agents Induce Mitochondrial Toxicity and Cell Death in Human Neurons, and Toxicity Increases With Reduced Kinetic Stability of the Agent https://t.co/fu7hd8fiON
— InvRadiologyOnline (@InvRadiologyOnl) July 8, 2019
"Intact GBCA are able to penetrate a series of brain barrier immediately after administration regardless the type of the chelate. Gadolinium may be bound with macromolecules that may cause Gd retention in the brain."
Quantitative analysis of Gd in the protein content of the brain following single injection of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) by size exclusion chromatographyhttps://t.co/RQWxFqRHhT#Radiology #Gadolinium pic.twitter.com/hVtBEwoP9t
— BJR Journals (@BJR_Radiology) July 6, 2019
"Gadolinium can be detected in both enhancing and non-enhancing gliomas, neighboring normal brain, and necrosis."
Gadolinium retention in gliomas and adjacent normal brain tissue: association with tumor contrast enhancement and linear/macrocyclic agents, by Kiviniemi et al. on May issue https://t.co/FprRuNGruz #NeuroRad #Gad pic.twitter.com/s3Rj0sZPed
— Neuroradiology (@NRADjournal) April 26, 2019
 Media Coverage
Media Coverage
Gadolinium-free imaging agent has strong potential as preferred contrast for MRI exams. @MassGeneralNews https://t.co/Ci4b1fq6Mc
— Health Imaging (@HealthImaging) December 15, 2020
“This spectacular improvement in the ability to non-invasively detect trace amounts of gadolinium in the brain by using quantitative susceptibility mapping verifies that macrocyclic GBCA accumulates in the brain,” -@WeillCornell editorialists https://t.co/2qUR3LwBZD
— Health Imaging (@HealthImaging) July 21, 2020
Could a manganese-based MRI contrast agent (MBCA) provide equivalent MR image quality and alleviate concerns around the use of #gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs)? New research indicates that it has some potential. #MRI #radiology https://t.co/NIOYuEUbib pic.twitter.com/Ml4PNXxOlo
— AuntMinnie.com (@AuntMinnie) January 10, 2020
Gadolinium was long thought to bypass the blood-brain barrier before settling in certain brain regions, but these findings suggest contrast may traffic alternate routes, potentially via the brain’s neurons and glial cells @RadiologyACR #gadolinium #GBCA https://t.co/irudSsEcoa
— Health Imaging (@HealthImaging) November 26, 2019
Disturbing news about gadolinium persistence in the environment, although the trace levels involved are believed to be far too low to pose a health risk. #MRI #radiology https://t.co/lyOpcFdNFi
— AuntMinnie.com (@AuntMinnie) August 29, 2019
 Reveal News
Reveal News
Eric Gale's Investigative Radiology paper Tumor Contrast Enhancement and Whole-Body Elimination of the Manganese-Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agent Mn-PyC3A is shortlisted for Scientific Paper of the Year